API Key File
Introduction
In Vigiles, users can generate a unique, secret API key per Organization. The key allows them to authenticate API requests without storing or entering their Vigiles account passwords directly. This key would not allow anyone to access their accounts on the web, but because one could impersonate them while using certain services, users should still treat the key like they would a password.
Once a key is created, a file containing it can be downloaded for use by Vigiles, Desktop Factory, TimeStorm, and other Timesys tools.
Do not share your API key with anyone! There are instructions below for protecting it and creating a new one if you feel that it has been compromised.
Obtaining a Key
Keys are created on the user profile page which is accessible from the user dropdown menu in the top navigation bar.
On the profile page, you can create a new API key, and download a key file for each Organization.
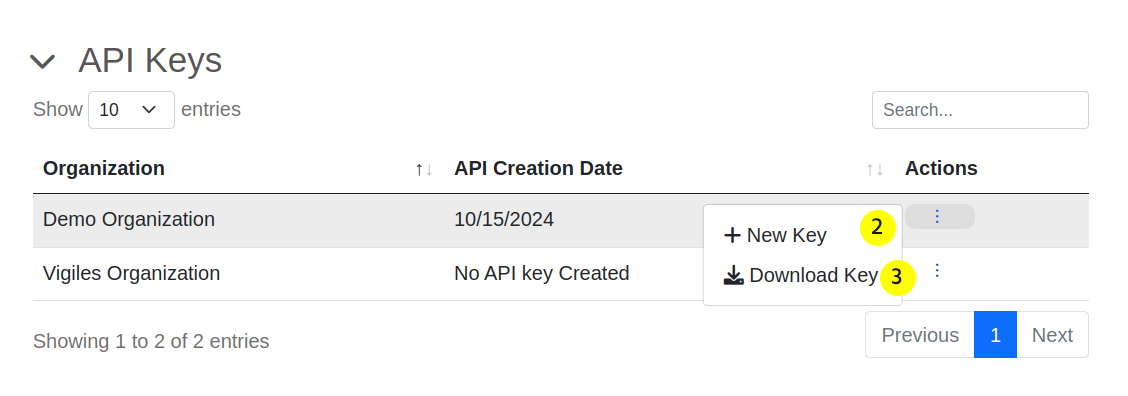 Note: If you believe your key has been compromised, generate a new one here immediately. Once a new key file is created, the previous one will no longer function.
Note: If you believe your key has been compromised, generate a new one here immediately. Once a new key file is created, the previous one will no longer function.
The Key File
The key file is a JSON-formatted file containing the user's email address, secret key, server URL, and enterprise set to true. Timesys tools such as the Desktop Factory will look to this file for credentials to use when making Vigiles API calls on your behalf.
File Location
The file should be named linuxlink_key (without a file extension) and saved to a folder called timesys in the user's home directory. e.g.:
/home/user/timesys/linuxlink_key
Many of our tools will expect to find the file in that location. In some cases the location may be overridden by an environment variable or configuration option. For example, checking for upstream updates in the Desktop Factory:
KEY_FILE=~/.linuxlink_key make checkupdates
When using Vigiles with Yocto, you may set the location in local.conf:
VIGILES_KEY_FILE = "/tools/timesys/linuxlink_key"
Protecting the Key
The API key, like a password, should remain secret (see the Introduction section for explanation).
It is therefore important to restrict access to the key file by making sure it is only readable or writable by the user:
chmod 600 ~/timesys/linuxlink_key
ls -l ~/timesys/linuxlink_key
-rw------- 1 user user 92 Sep 29 14:49 /home/user/timesys/linuxlink_key